CPSC 330 Lecture 16: Recommender Systems
Rest of CPSC 330
We started CPSC 330 with Machine Learning fundamentals, Supervised Learning models, Unsupervised Learning models, more complex fundamentals like feature engineering and feature selection
We are now ready to try and solve different types of problems! - Today: Recommender Systems - Next class: Text Data and Topic Modelling - After: Images and Computer vision, Time Series Data, etc…
iClicker 16.0
What percentage of the total watch time on YouTube do you think comes from reccomendations?
- 20%
- 50%
- 70%
- 95%
What is a Recommender System?
A recommender or a recommendation system recommends a particular product or service to users they are likely to consume.
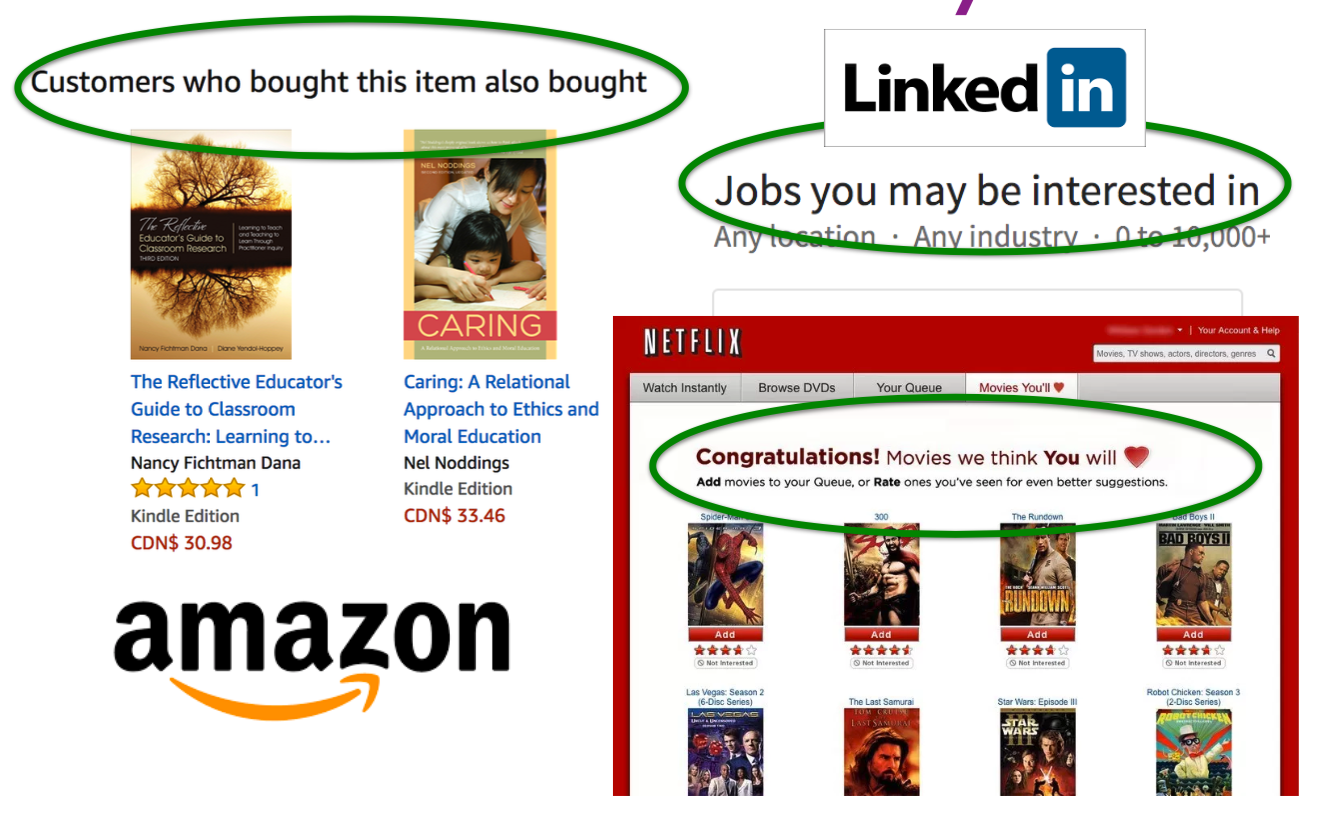
Examples of Recommender Systems
- Amazon
- Netflix
- Tinder
- etc…
What should be shown to the user so they buy more products/spend more time on the app/etc…
Ethics of Recommender Systems
We should be very mindful of the drawbacks of relying on recommender systems.
What are some ethical considersations of recommender systems?
What comprises a recommender system?
What does the problem formulation look like?
What tools would/should we use to create a recommender system?
Notebook for Lecture 17
Break
Let’s take a 10 min break
iClicker Exercise 16.1
Select all of the following statements which are True (iClicker)
- In the context of recommendation systems, the shapes of validation utility matrix and train utility matrix are the same.
- RMSE perfectly captures what we want to measure in the context of recommendation systems.
- It would be reasonable to impute missing values in the utility matrix by taking the average of the ratings given to an item by similar users.
- In KNN type imputation, if a user has not rated any items yet, a reasonable strategy would be recommending them the most popular item.
